Michael's Hands
Bone Cancer
| By: Michael Manion | Viewed: 3/2/2026 |
Topics/Keywords: #BoneCancer #Cancer #Health | Page Views: 6646 |
| All about bone cancer. | |||
Cancer that arises in the bone (primary bone cancer) is not the same disease as cancer that spreads to the bone from another part of the body (secondary bone cancer). Primary bone cancer is rare, with only about 2,500 new cases diagnosed each year in the United States. More commonly, bones can be the site of tumors that result from the spread (metastasis) of cancer from another organ, such as the breasts, lungs, or prostate.
The most common type of bone cancer is osteosarcoma, which develops in new tissue in growing bones. Another type of cancer, chondrosarcoma, arises in cartilage. Evidence suggests that Ewing's sarcoma, which is another form of bone cancer, begins in immature nerve tissue in bone marrow. Osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma tend to occur more frequently in children and adolescents, while chondrosarcoma occurs more often in adults.
| Types of Cancer | Tissue of Origin | Common Locations | Common Ages |
| Osteosarcoma | Osteoid | Knees, upper legs, upper arms | 10-25 |
| Chondrosarcoma | Cartilage | Pelvis, upper legs, shoulders | 50-60 |
| Ewing's Sarcoma | Immature nerve tissue, usually in bone marrow | Pelvis, upper legs, ribs, arms | 10-20 |
Bone cancers occur more frequently in children and young adults, particularly those who have had radiation or chemotherapy treatments for other conditions. Adults with Paget's disease, a noncancerous condition characterized by abnormal development of new bone cells, may be at increased risk for osteosarcoma. A small number of bone cancers are due to heredity. For example, children with hereditary retinoblastoma (an uncommon cancer of the eye) are at a higher risk of developing osteosarcoma.
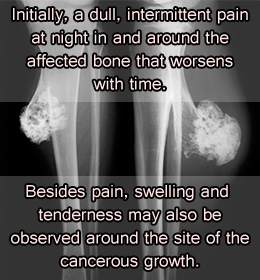
Pain is the most common symptom of bone cancer. However, symptoms may vary depending on the location and size of the tumors. Tumors that occur in or near joints may cause swelling or tenderness in those areas. Bone cancer can also interfere with normal movements and can weaken the bones, occasionally leading to a fracture or fractures. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and anemia.
©1998-2026 Michael Manion
All Rights Reserved
